Web designing in a powerful way of just not an only professions. We have tendency to believe the idea that smart looking .
Maintaining good oral and dental care is crucial for overall health and well-being. Healthy teeth and gums not only contribute to a beautiful smile but also prevent various dental problems such as tooth decay, gum disease, and bad breath. Additionally, poor oral health can be linked to serious health issues such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
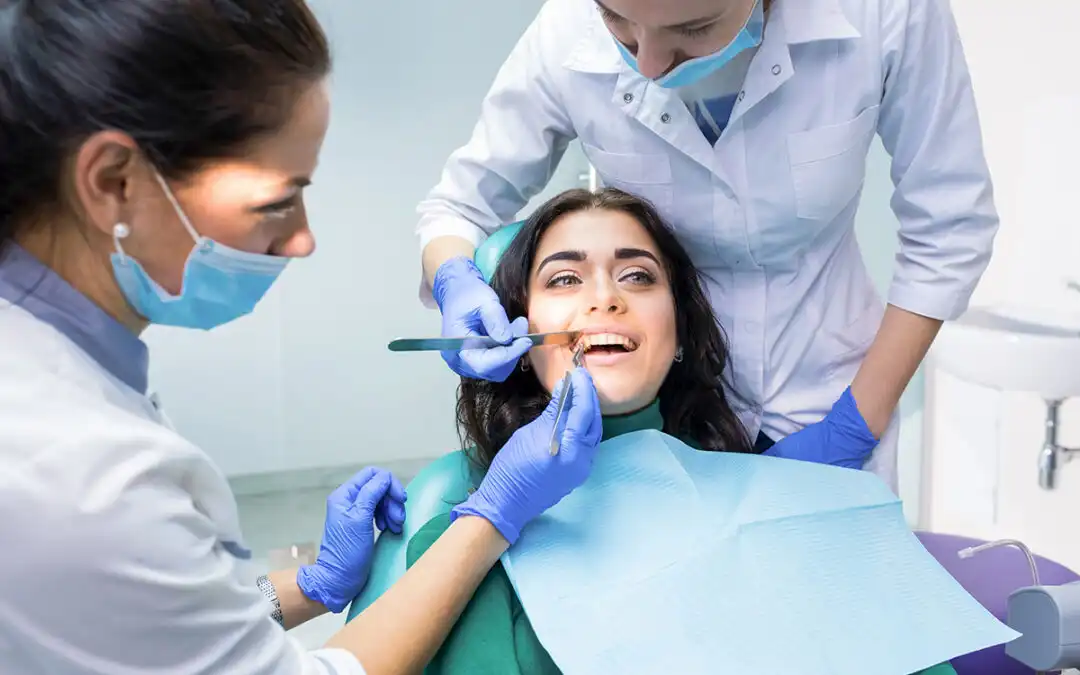
Replace your toothbrush every 3-4 months, or sooner if the bristles are frayed. A worn toothbrush is less effective at cleaning teeth.
Both can be effective if used properly, but electric toothbrushes may make it easier to clean teeth thoroughly and are often recommended for people with limited manual dexterity.
Over-the-counter whitening products can be effective, but it's best to consult your dentist for professional whitening treatments that are safe and tailored to your needs.
Contact your dentist immediately if you experience severe pain, swelling, or trauma to your teeth or gums. For after-hours emergencies, visit an emergency dental clinic.
Dental X-rays use very low levels of radiation and are generally safe. Dentists take precautions to minimize exposure, and the benefits of diagnosing dental issues early far outweigh the risks.
